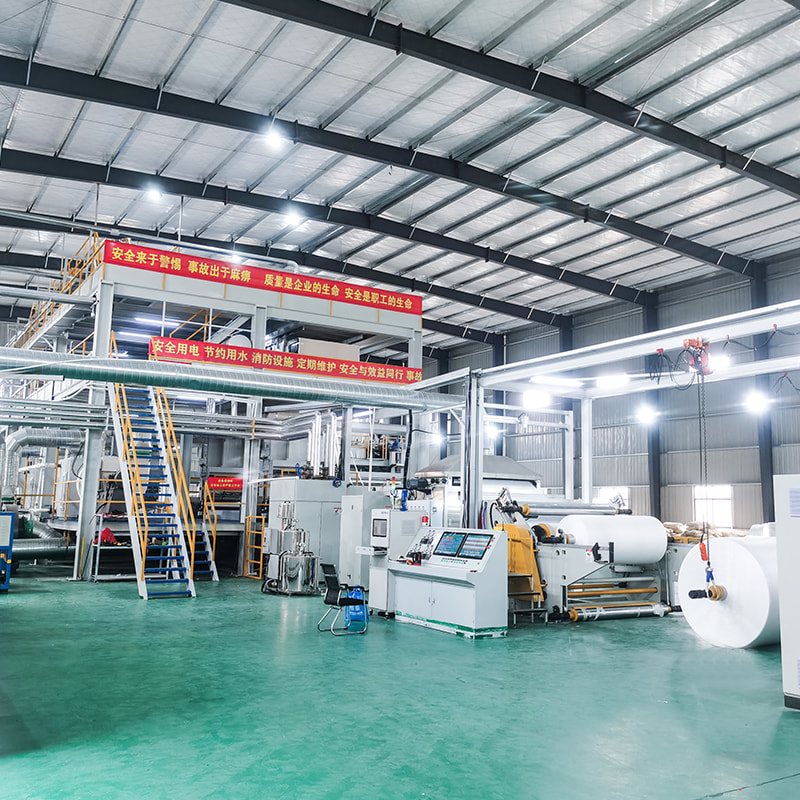
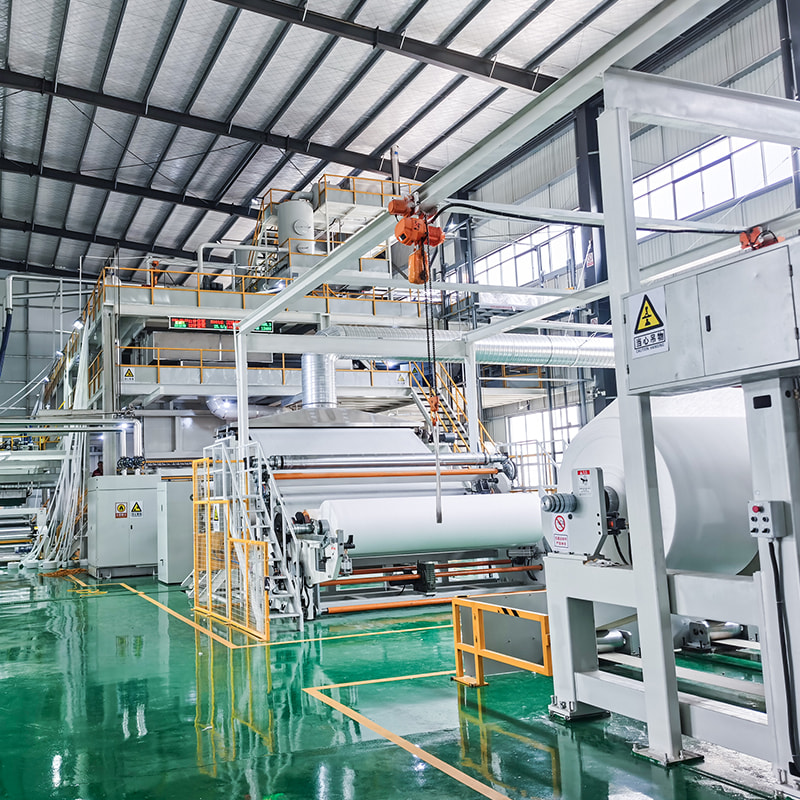
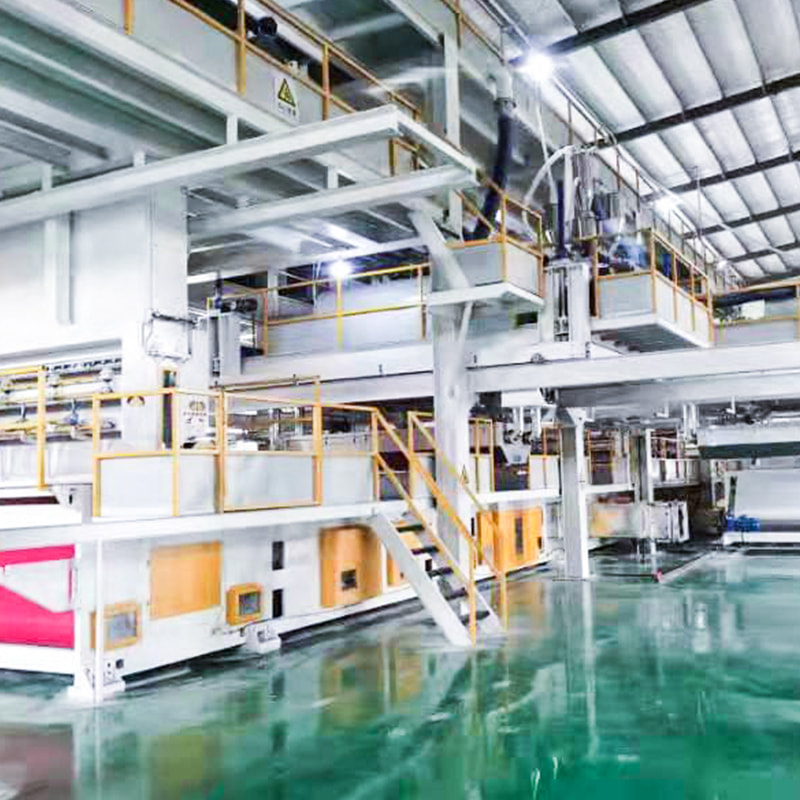
How Filament Denier Influences Fabric Quality and Application in Spunbond Nonwoven Machines
In the world of nonwoven production, filament denier plays a crucial role in determining the final fabric’s texture, strength, and suitability for various end uses. For manufacturers investing in a spunbond nonwoven machine, understanding how filament denier affects the process and product is key to achieving consistent quality and meeting specific application needs. Typically, spunbond lines operate within a filament denier range of 1.8 to 2.5D, a window carefully selected to balance strength and softness across a variety of fabric weights.
Filament denier refers to the thickness of the individual polypropylene filaments extruded through the machine. A lower denier results in finer, softer filaments that are ideal for hygiene and medical-grade fabrics, where comfort and barrier properties are essential. On the other hand, a slightly higher denier produces stronger and more robust fabrics, often required in agriculture, geotextile, and industrial packaging applications. The versatility of the spunbond process lies in its ability to adjust denier according to final product demands, which is why machine configuration and process control are so important.
In a high-performance spunbond nonwoven machine, precise melt control, spinneret design, and quenching air parameters collectively determine filament consistency. If filament uniformity is compromised, it can lead to uneven fabric surface, reduced mechanical strength, or even defects in the bonding process. Manufacturers with deep experience in thermal bonding and air drawing systems know that even small fluctuations in denier can impact both aesthetics and function, which is why quality-focused production lines put a strong emphasis on denier control systems.
Modern spunbond nonwoven machines are equipped with advanced feedback mechanisms to regulate denier within the required tolerance. It’s not just about producing fabric—it’s about producing usable fabric that passes real-world performance tests. Customers in sectors like medical and automotive manufacturing often require certification-grade outputs, and meeting those standards starts with getting the filament right. Denier is more than a number; it’s a benchmark of both machine precision and raw material compatibility.
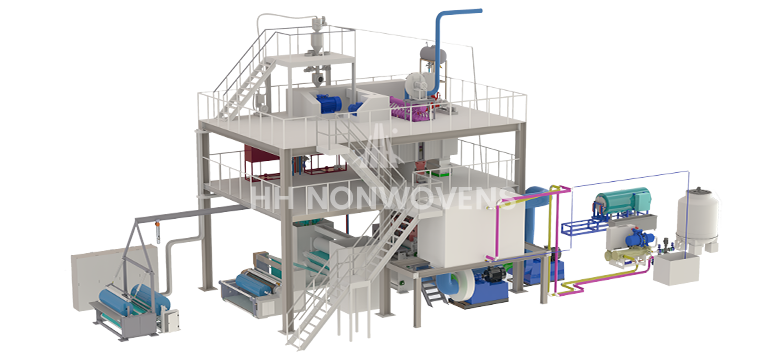
At JIASHAN HH Nonwovens Machinery Co., Ltd, we understand that filament control is one of the top priorities for clients aiming to meet market-specific needs. Our spunbond nonwoven machine designs incorporate finely tuned extruder systems and balanced spinneret arrangements, enabling stable denier output across different fabric widths and weights. Whether you're producing 9gsm hygiene wraps or 70gsm crop covers, we offer scalable solutions that match your performance requirements.
Choosing the correct denier also impacts downstream processes like lamination, printing, and ultrasonic welding. If the filament is too thick or too thin for the application, the final product may fail in field conditions or exhibit poor adhesion in multilayer structures like SMS or SMMS composites. A quality spunbond nonwoven machine gives you control not just over the base fabric, but over the entire value chain of your nonwoven products.
While filament denier might seem like a minor technical detail, it actually carries major implications for production efficiency, cost control, and customer satisfaction. That’s why experienced suppliers focus on optimizing every step, from polymer feeding to filament formation. Investing in a machine that delivers denier stability is ultimately an investment in your brand reputation and product reliability.
If you’re looking to upgrade your production or expand into new application markets, understanding filament denier’s role is a great place to start. Let our team help you configure a spunbond nonwoven machine that matches your business goals with precision and confidence.






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





