Introduction of PP Nonwoven Fabric Machinery: Structure & Applications
Overview of PP Nonwoven Fabric Machinery
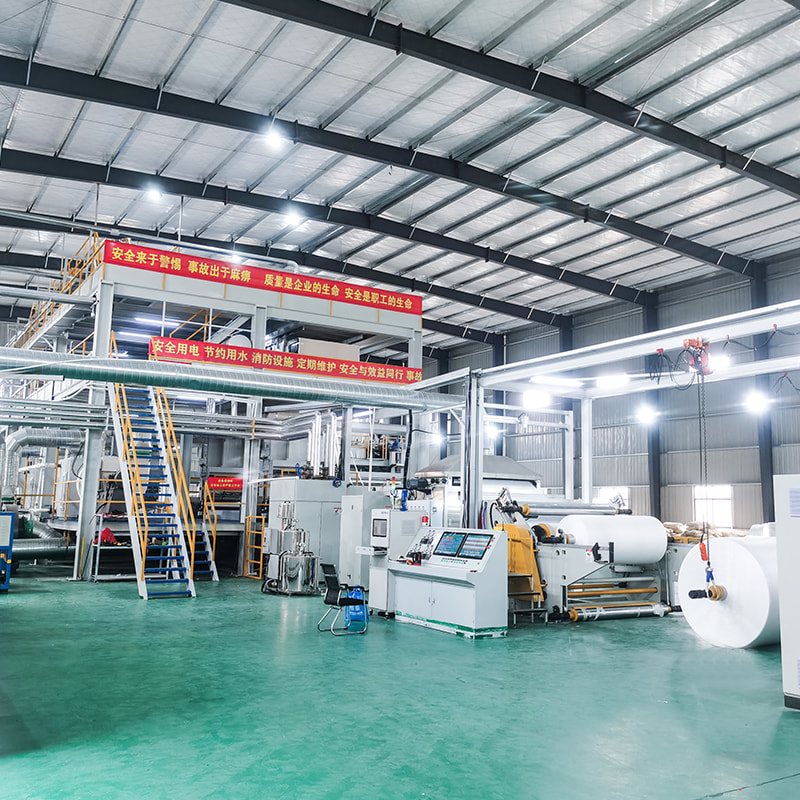
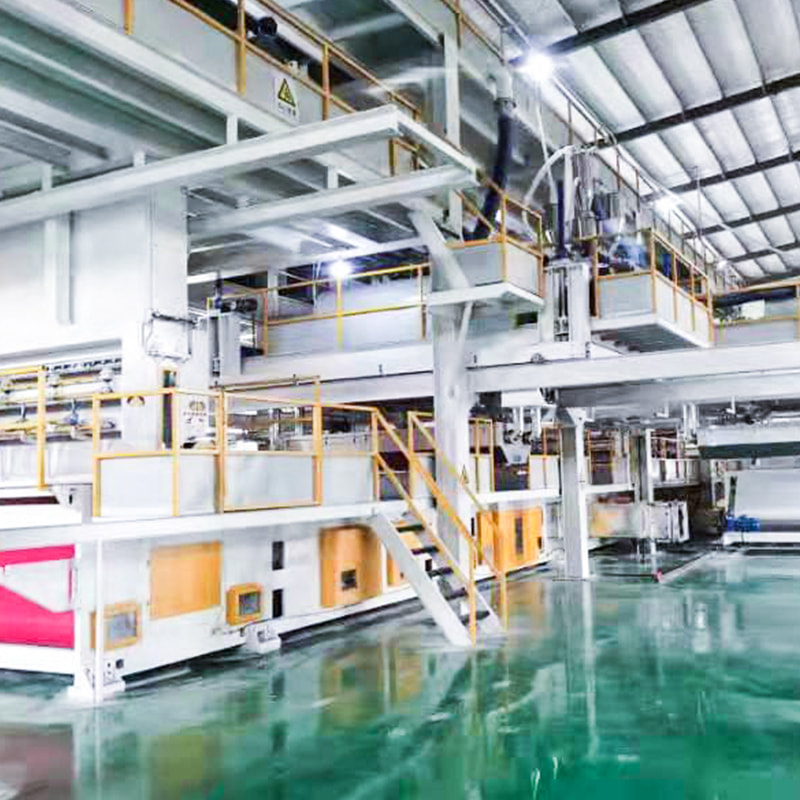
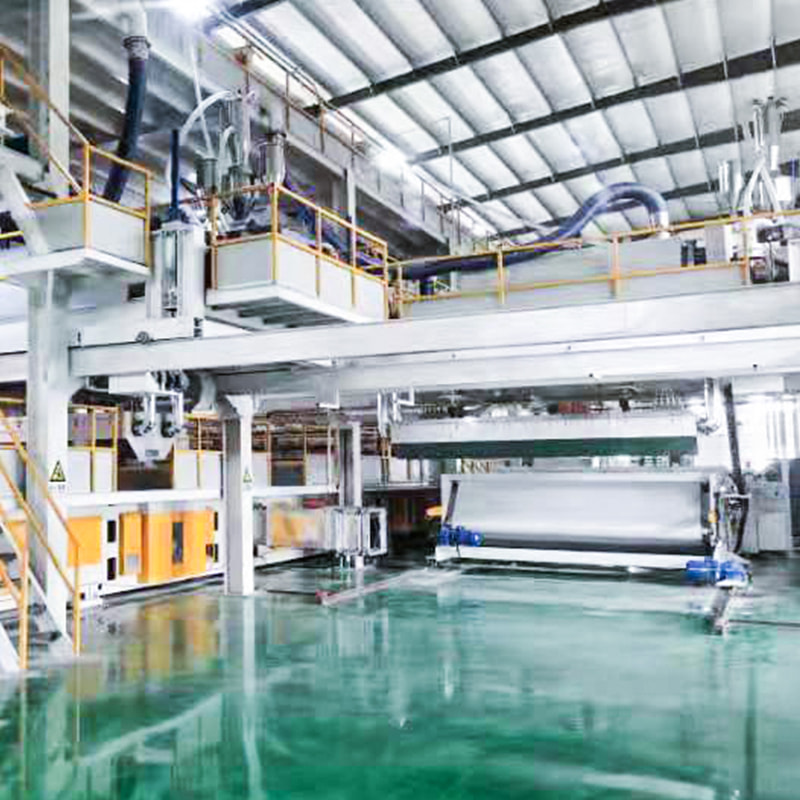
PP nonwoven fabric machinery refers to industrial equipment designed to manufacture polypropylene-based nonwoven fabrics through continuous, automated processes. These machines convert polypropylene granules into finished fabric without traditional weaving or knitting. The resulting material is lightweight, breathable, cost-effective, and suitable for large-scale production.
Modern PP nonwoven machinery is widely used in medical supplies, hygiene products, agriculture, packaging, and construction. Production lines typically operate at speeds ranging from 300 to 800 meters per minute, depending on fabric weight and machine configuration.
Core Components of PP Nonwoven Fabric Machinery
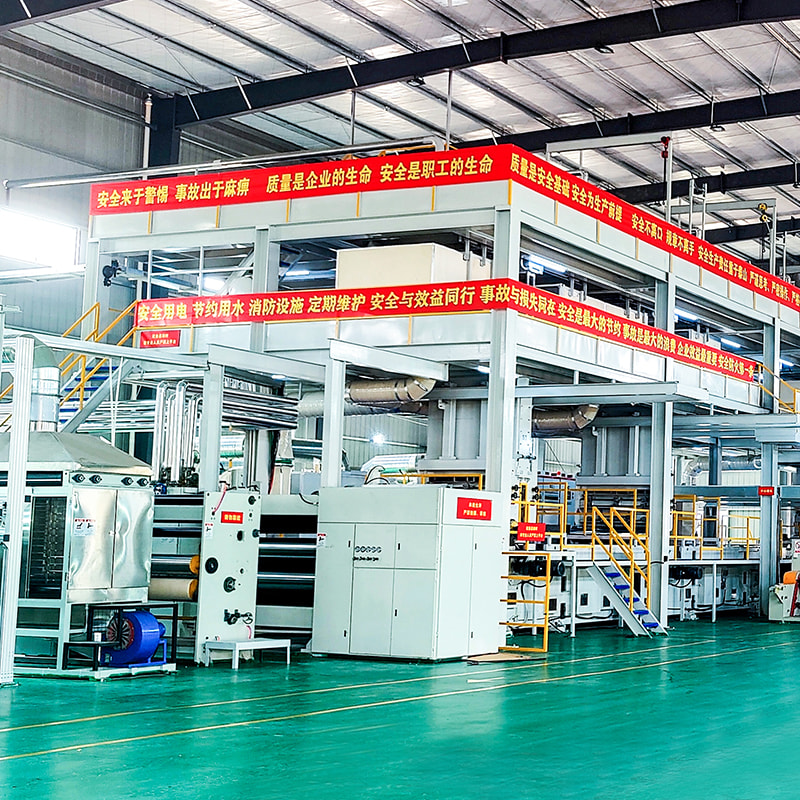
A standard PP nonwoven fabric production line consists of multiple integrated systems working in sequence. Each component directly affects fabric uniformity, strength, and output stability.
Main Mechanical and Process Units
- Extruder system that melts polypropylene granules at temperatures between 220–260°C
- Spin beam and spinneret for filament extrusion and diameter control
- Quenching and drawing unit to cool and stretch fibers for tensile strength
- Web forming section that evenly distributes filaments onto a conveyor
- Bonding system, typically thermal calender bonding
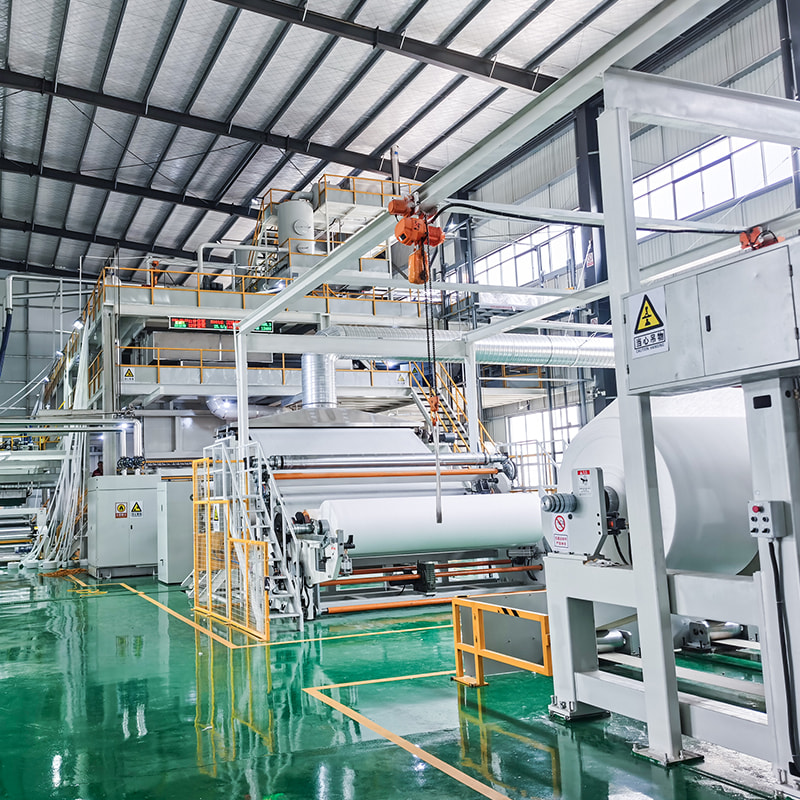
- Winding and cutting unit for finished fabric rolls
Production Process Flow of PP Nonwoven Fabric
The production process of PP nonwoven fabric machinery follows a continuous and highly controlled workflow. Automation minimizes human intervention while ensuring consistency in fabric quality.
Step-by-Step Manufacturing Flow
- Polypropylene granules are fed into the extruder and melted
- Molten polymer is filtered and pumped through spinnerets
- Filaments are cooled, drawn, and stretched
- Fibers are laid randomly or directionally to form a web
- Thermal bonding solidifies the fabric structure
- Fabric is trimmed, rolled, and packaged
Technical Specifications and Output Parameters
Output capacity and fabric characteristics depend on machine width, spinning technology, and bonding method. The table below summarizes common industrial specifications.
| Parameter | Standard Range |
|---|---|
| Fabric Weight | 10–200 GSM |
| Machine Width | 1.6–3.2 meters |
| Production Speed | 300–800 m/min |
| Daily Output | 8–20 tons |
| Energy Consumption | 600–800 kWh/ton |
Common Applications of PP Nonwoven Fabrics
PP nonwoven fabrics produced by specialized machinery are valued for their versatility and cost efficiency. Different industries utilize specific fabric weights and bonding strengths.
- Medical and hygiene: surgical masks, gowns, disposable caps
- Agriculture: crop covers, weed control fabrics
- Packaging: shopping bags, protective wrapping
- Furniture and bedding: mattress layers, sofa linings
- Construction: geotextiles and insulation layers
Key Advantages of Modern PP Nonwoven Fabric Machinery
Advances in automation and process control have significantly improved the efficiency of PP nonwoven fabric machinery over the past decade.
- High production efficiency with minimal labor requirements
- Stable fabric uniformity due to precise temperature and airflow control
- Flexible adjustment for different GSM and fabric widths
- Lower material waste compared to woven fabric processes
- Scalable production suitable for mass manufacturing






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





