PP Spunbonded Non-Woven Fabric: A Deep Dive into Its Properties, Production, and Applications
Introduction
Polypropylene (PP) spunbonded non-woven fabric, a staple in the textile and industrial sectors, has carved out a vital niche due to its versatile properties and wide-ranging applications. As an engineered fabric, PP spunbonded non-woven fabric has proven its significance in numerous industries, including healthcare, automotive, agriculture, and fashion. But what exactly makes this fabric so useful, and why has it become a key material in such a variety of applications?
In this article, we’ll explore the composition, manufacturing process, properties, and applications of PP spunbonded non-woven fabric, highlighting its role in modern technology, industry, and sustainability.
What is PP Spunbonded Non-Woven Fabric?
Non-woven fabrics are materials made from fibers that are bonded together by mechanical, chemical, or thermal means, rather than woven or knitted. PP spunbonded non-woven fabric refers to a non-woven fabric made primarily from polypropylene (PP) fibers that are formed through a spunbonding process.
In the spunbonding process, polypropylene resin is melted and extruded into fine filaments. These filaments are then laid out on a moving belt and bonded together through heat and pressure, forming a fabric-like material. The result is a strong, durable, and versatile fabric with numerous advantages over traditional woven fabrics.
Key Characteristics of PP Spunbonded Non-Woven Fabric
Durability and Strength: PP spunbonded fabrics are known for their tensile strength, making them highly resistant to tearing, abrasion, and deformation. This durability is critical for applications where the fabric must endure heavy use or extreme conditions.
Lightweight: Despite its strength, PP spunbonded fabric is incredibly lightweight, which contributes to its low cost and ease of handling.
Breathability: Non-woven PP fabrics possess excellent air permeability, making them ideal for medical applications, such as surgical gowns and face masks, where breathability is crucial.
Water and Chemical Resistance: Polypropylene itself is resistant to water and many chemicals, allowing spunbonded fabrics to be used in environments exposed to moisture, oils, and acids.
Cost-Effective: Compared to woven fabrics, PP spunbonded non-woven fabric is relatively inexpensive to produce, making it a highly cost-effective solution for mass production and industrial applications.
Softness: When processed correctly, PP spunbonded fabrics can maintain a soft texture, making them suitable for use in personal care items such as diapers, wet wipes, and sanitary napkins.
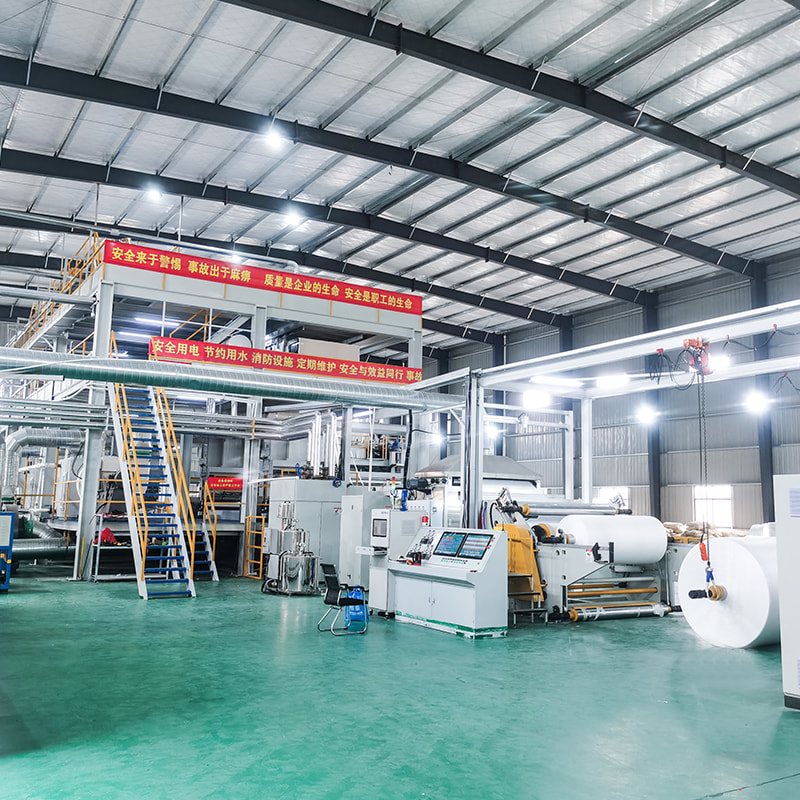
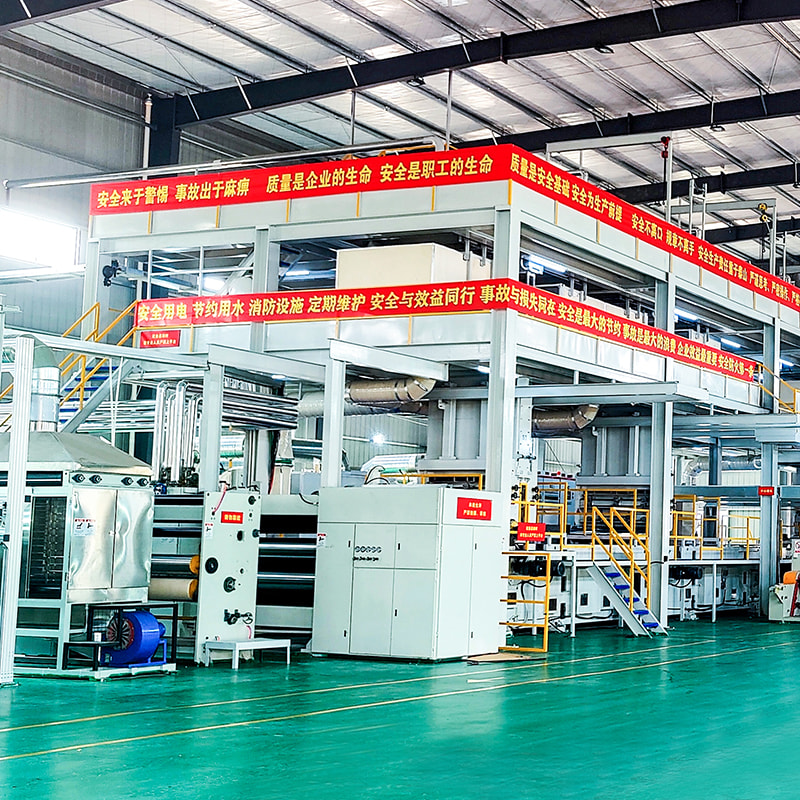
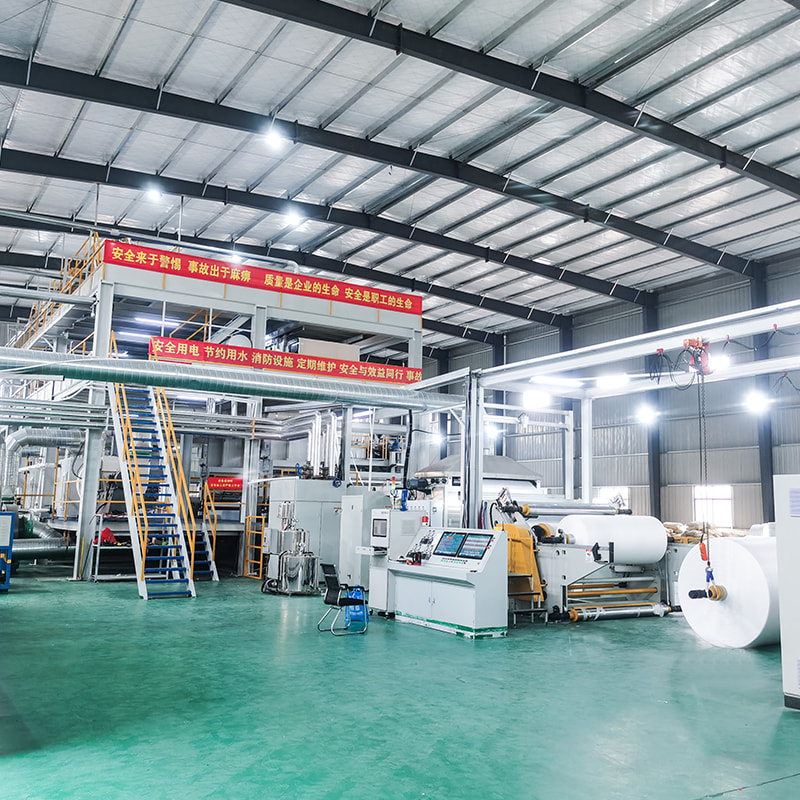
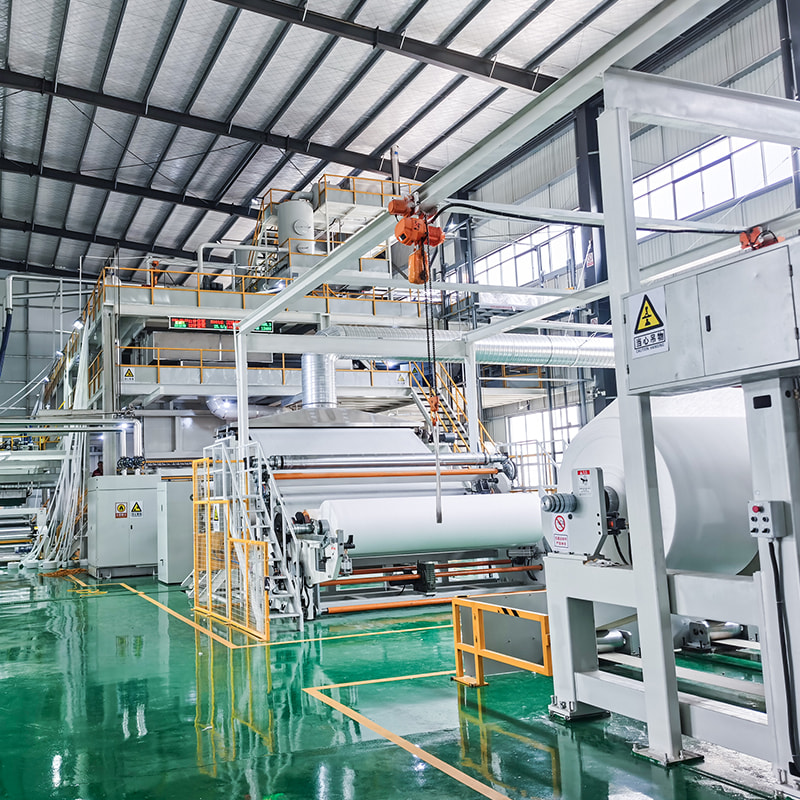
Manufacturing Process of PP Spunbonded Non-Woven Fabric
The production of PP spunbonded non-woven fabric involves several steps:
Polymerization and Melting: Polypropylene pellets are fed into an extruder, where they are melted at high temperatures (typically around 250°C). This molten polymer is then spun into fine filaments.
Spinning: The molten polypropylene is forced through spinnerets, which are devices that shape the liquid polymer into fine fibers. These fibers are then cooled and solidified.
Web Formation: The filaments are collected on a conveyor belt and randomly laid down to form a web. The fibers can either be deposited in a continuous or random manner, depending on the desired characteristics of the final fabric.
Bonding: The web of fibers is then subjected to heat and pressure, which bonds the fibers together to form a solid sheet of non-woven fabric. The bonding process can be accomplished through different techniques, including thermal bonding (using heat), chemical bonding (with adhesives), or mechanical bonding (using needle punching or hydroentangling).
Finishing: The fabric may undergo further treatments such as dyeing, calendaring, or adding functional finishes to enhance its properties (e.g., water repellency or flame resistance).
Applications of PP Spunbonded Non-Woven Fabric
The unique properties of PP spunbonded non-woven fabric have made it indispensable in many industries. Let’s explore some of its key applications:
1. Healthcare and Medical Industry
PP spunbonded non-woven fabric plays a critical role in healthcare, particularly in disposable medical products:
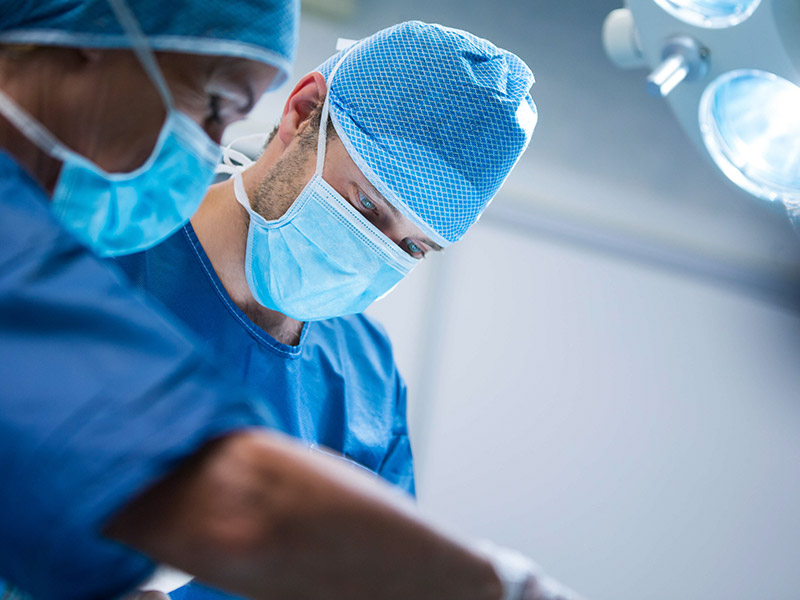
Surgical Gowns and Masks: PP spunbonded fabrics are widely used for surgical gowns, face masks, and other personal protective equipment (PPE). Their breathable, lightweight, and impermeable nature makes them ideal for maintaining hygiene and reducing the risk of infection.
Wound Dressings and Sterile Wraps: Non-woven fabrics are used for sterile wraps, bandages, and wound dressings due to their ability to offer protection without compromising breathability and comfort.
2. Agriculture
In the agricultural sector, PP spunbonded non-woven fabric is used extensively for:
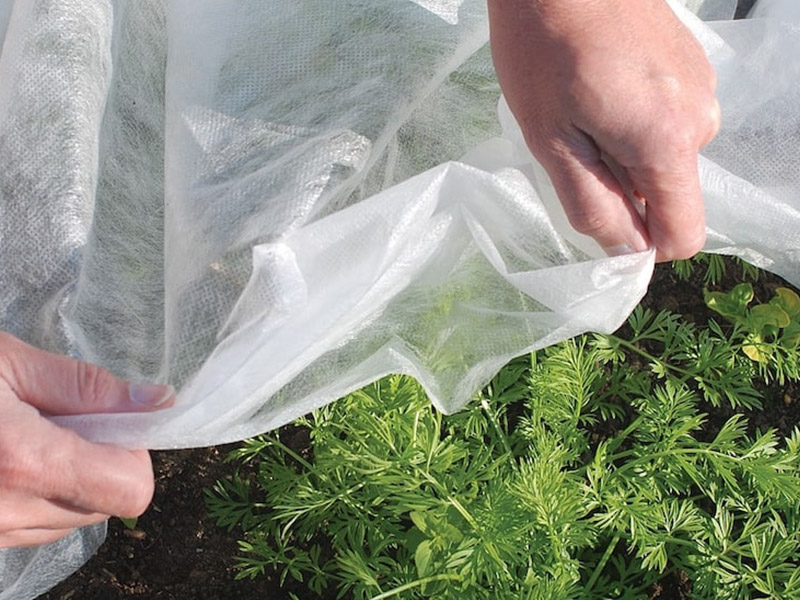
Crop Protection: It serves as a protective covering for crops, shielding them from pests, extreme weather, and disease while allowing sunlight and water to penetrate.
Geotextiles: Used for soil stabilization, erosion control, and drainage systems, PP spunbonded fabrics help manage soil integrity and prevent erosion.
3. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry benefits from PP spunbonded fabrics in various components:
Interior Fabrics: These fabrics are used in car seats, headliners, door panels, and trunk liners, where durability, lightweight, and comfort are key considerations.
Sound Insulation: Non-woven fabrics are also utilized in soundproofing applications, where their absorbent properties reduce road noise and improve cabin comfort.
4. Fashion and Apparel
Though less common than other textile materials, PP spunbonded fabric is also used in fashion and apparel:
Fashion Accessories: The fabric can be used to make eco-friendly bags, hats, and shoes.
Sustainable Fashion: With growing interest in sustainable textiles, PP spunbonded non-woven fabric offers a low-cost and recyclable alternative for manufacturers in the eco-fashion space.
5. Personal Care and Hygiene Products
PP spunbonded fabric is frequently used in the production of personal care items:
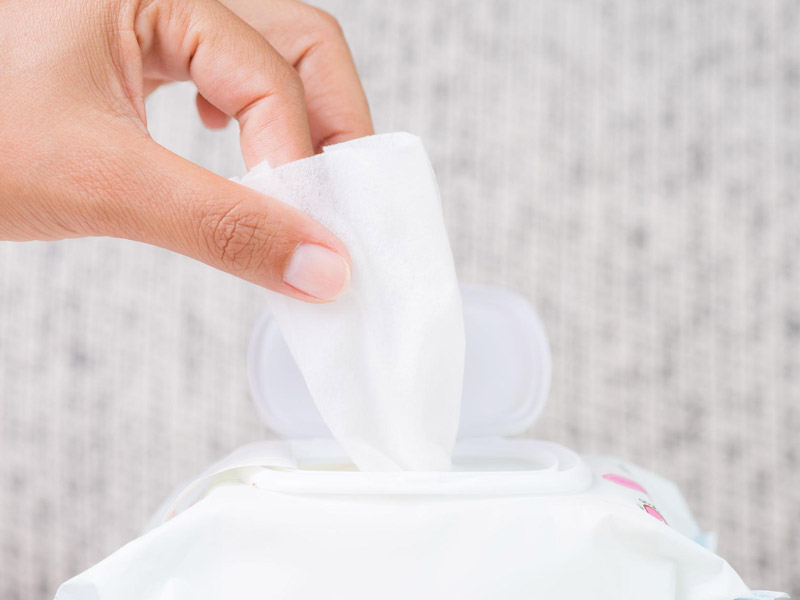
Diapers and Baby Wipes: Due to its softness, moisture-wicking properties, and low cost, PP spunbonded fabric is ideal for use in baby diapers and adult incontinence products.
Sanitary Napkins: The fabric is commonly used in the production of sanitary napkins due to its absorbency, comfort, and hypoallergenic properties.
6. Packaging
PP spunbonded non-woven fabric is employed in packaging materials, especially for:
Protective Covers: It is used to create protective covers for furniture, appliances, and automotive parts during transportation.
Reusable Shopping Bags: Due to the increasing demand for eco-friendly alternatives to plastic bags, PP spunbonded fabric is widely used to manufacture durable, reusable shopping bags.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer, meaning it can be recycled, though the recycling process for non-woven fabrics is more complicated than that of woven textiles. However, the fact that PP spunbonded non-woven fabrics are typically lightweight and durable makes them a more sustainable choice compared to some other materials, particularly in single-use applications. Moreover, PP non-wovens can be produced with minimal waste during the manufacturing process, which helps in reducing their environmental footprint.
However, because many of these fabrics are not biodegradable, their long-term impact on the environment remains a concern, especially when they are used in products like single-use medical supplies, packaging, and personal care items. Efforts are being made to improve the recyclability of PP spunbonded fabrics and increase their use in sustainable, eco-friendly products.






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





