What is Spunbond Nownoven Machine?
What a Spunbond Nonwoven Machine Is and Why It Matters
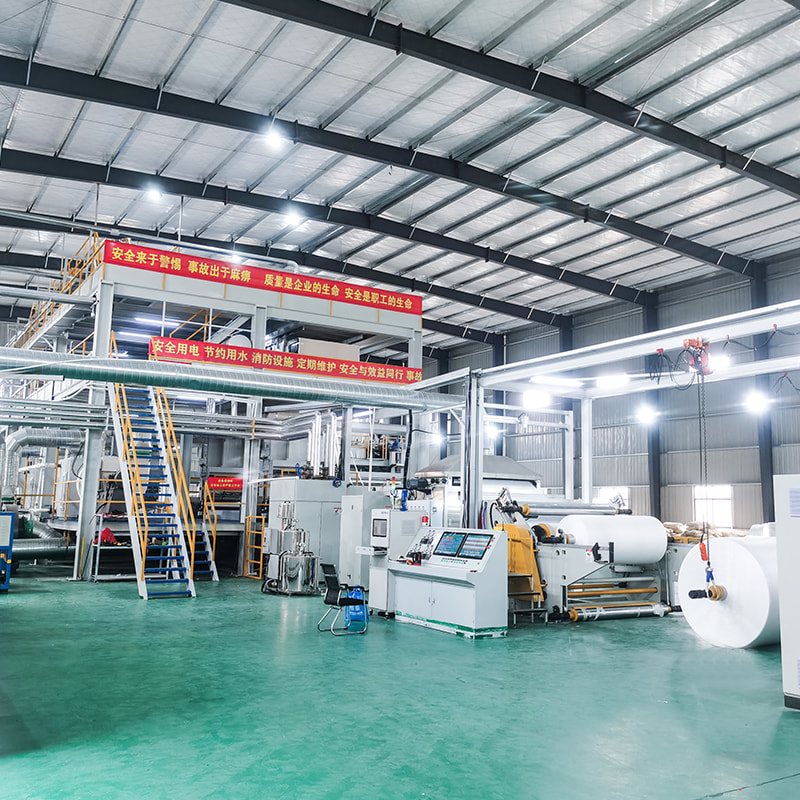
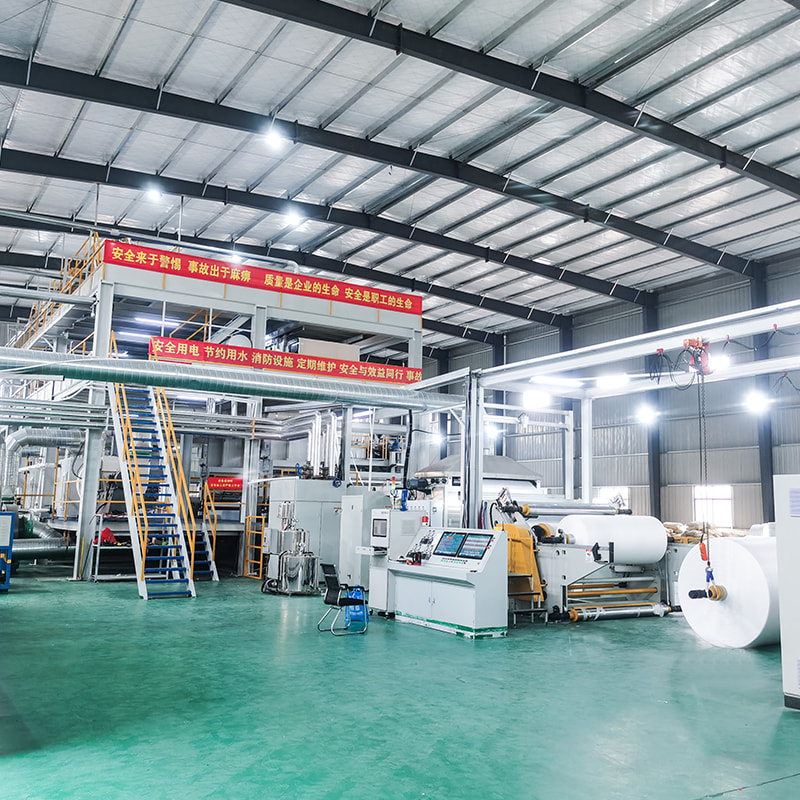
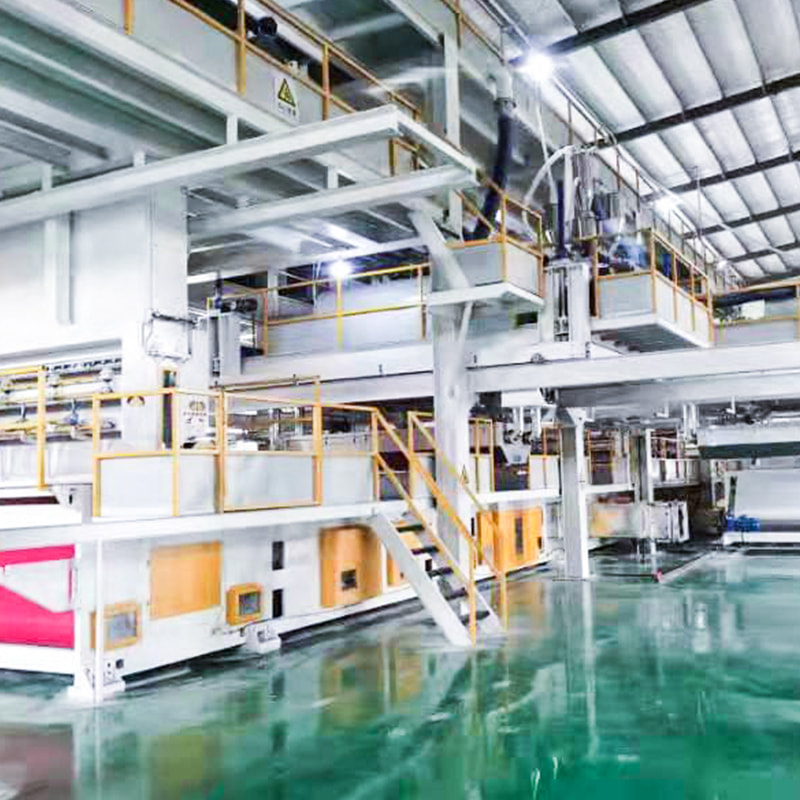
A spunbond nonwoven machine is industrial equipment designed to produce nonwoven fabrics by extruding thermoplastic polymers into continuous filaments, laying them into a web, and bonding them into a stable fabric. Unlike woven or knitted textiles, spunbond nonwovens are made in a single continuous process, which significantly reduces production time and cost.
These machines are widely used in industries such as hygiene, medical, agriculture, packaging, and construction because they deliver high output, consistent fabric quality, and excellent tensile strength.
Core Working Principle of a Spunbond Nonwoven Machine
The spunbond process integrates polymer melting, filament spinning, web forming, and bonding into one streamlined production line. This integration is what makes spunbond technology suitable for large-scale manufacturing.
Step-by-Step Production Flow
- Polymer chips (commonly polypropylene) are melted at temperatures around 220–260°C.
- The molten polymer is extruded through spinnerets to form continuous filaments.
- High-speed air drawing stretches the filaments, improving strength and uniformity.
- Filaments are laid randomly onto a moving conveyor to form a web.
- Thermal bonding calenders fuse the fibers, creating finished nonwoven fabric.
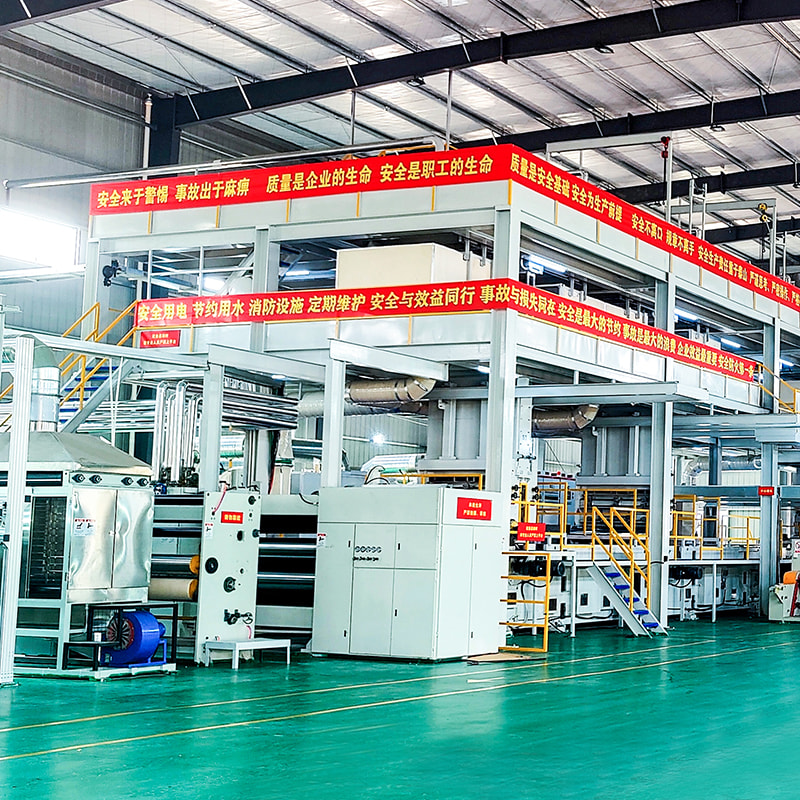
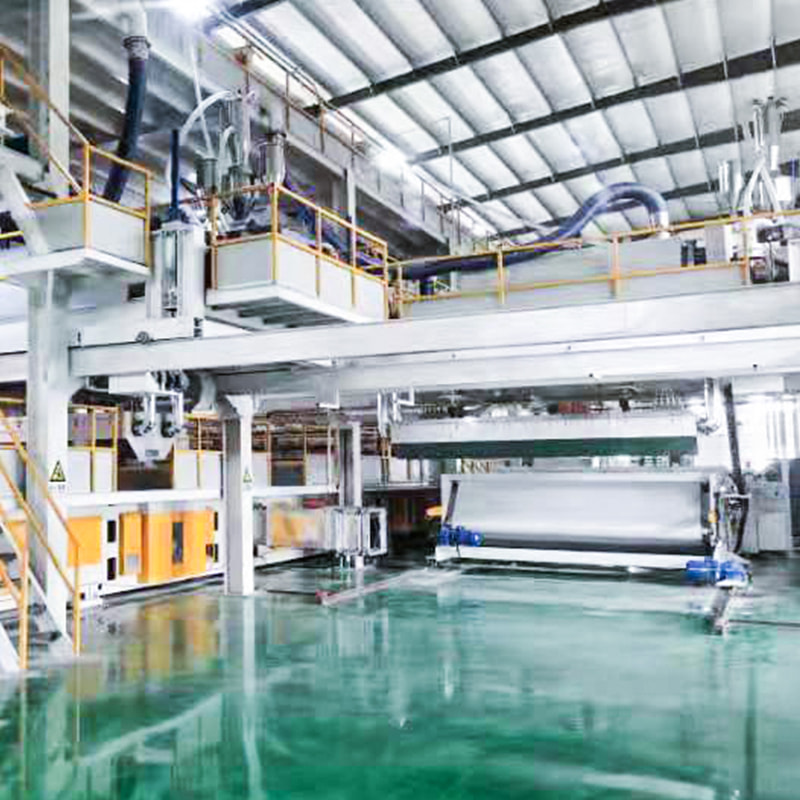
Main Components and Their Functions
Each section of a spunbond nonwoven machine plays a precise role in ensuring fabric performance and production efficiency.
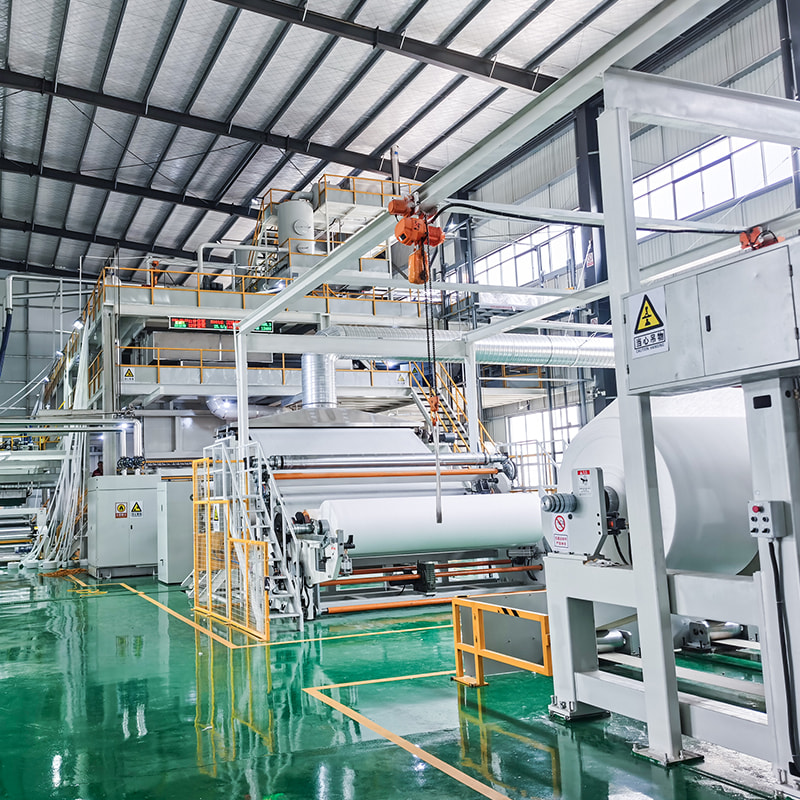
- Extruder system: Melts and delivers polymer at stable pressure and temperature.
- Spinneret assembly: Controls filament diameter, typically ranging from 15–35 microns.
- Air drawing unit: Uses compressed air to stretch filaments for higher tensile strength.
- Web forming section: Distributes filaments evenly to control fabric uniformity.
- Thermal bonding calender: Bonds fibers using heated rollers, defining fabric softness or rigidity.
Typical Technical Specifications and Output Capacity
Understanding machine specifications helps manufacturers select the right configuration for their target market and production scale.
| Parameter | Common Range |
|---|---|
| Fabric width | 1.6 m – 3.2 m |
| Fabric weight (GSM) | 10 – 200 GSM |
| Daily output | 8 – 25 tons |
| Raw material | Polypropylene (PP) |
Key Applications Across Industries
Spunbond nonwoven fabrics produced by these machines are valued for their balance of strength, breathability, and cost efficiency.
- Medical and hygiene: Surgical masks, disposable gowns, diapers, and sanitary products.
- Agriculture: Crop covers, weed control fabric, and soil protection layers.
- Packaging: Reusable shopping bags and protective wrapping materials.
- Construction: Roofing membranes, geotextiles, and insulation layers.
Practical Advantages for Manufacturers
Investing in a spunbond nonwoven machine offers both operational and commercial benefits, especially for high-volume production environments.
- High production efficiency with continuous operation and minimal labor input.
- Lower per-unit cost compared to woven textile manufacturing.
- Flexible fabric customization by adjusting GSM, width, and bonding patterns.
- Strong market demand driven by hygiene and medical consumption growth.






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





