Melt Blown Nonwoven Fabric: Properties, Applications & Manufacturing
Introduction to Melt Blown Nonwoven Fabric
Melt blown nonwoven fabric is a highly versatile material produced from thermoplastic polymers. It is distinguished by its ultra-fine fibers, excellent filtration capabilities, and lightweight structure. This fabric plays a crucial role in medical, industrial, and environmental applications.
Manufacturing Process
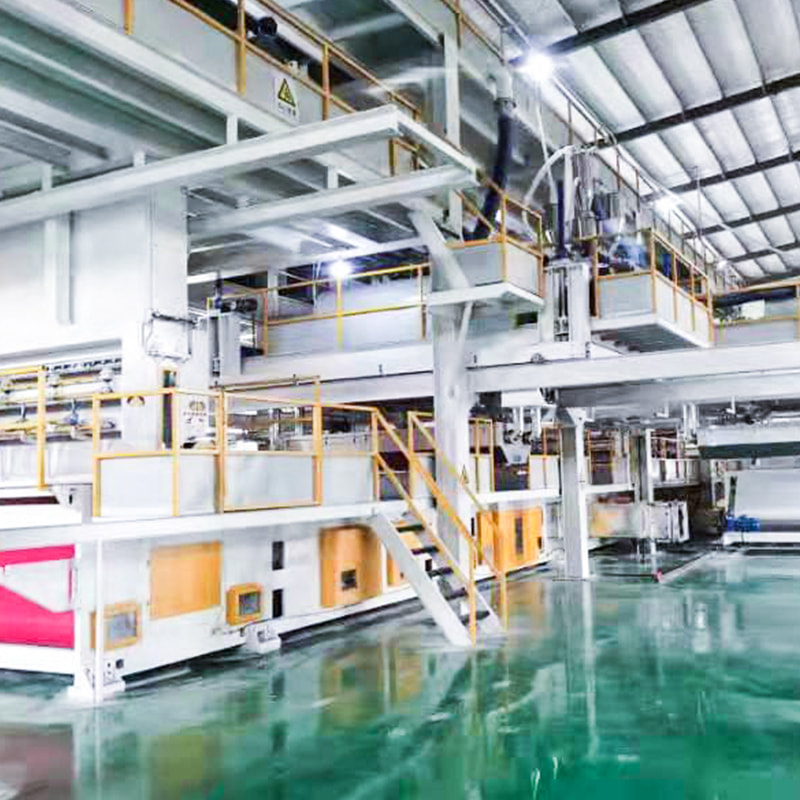
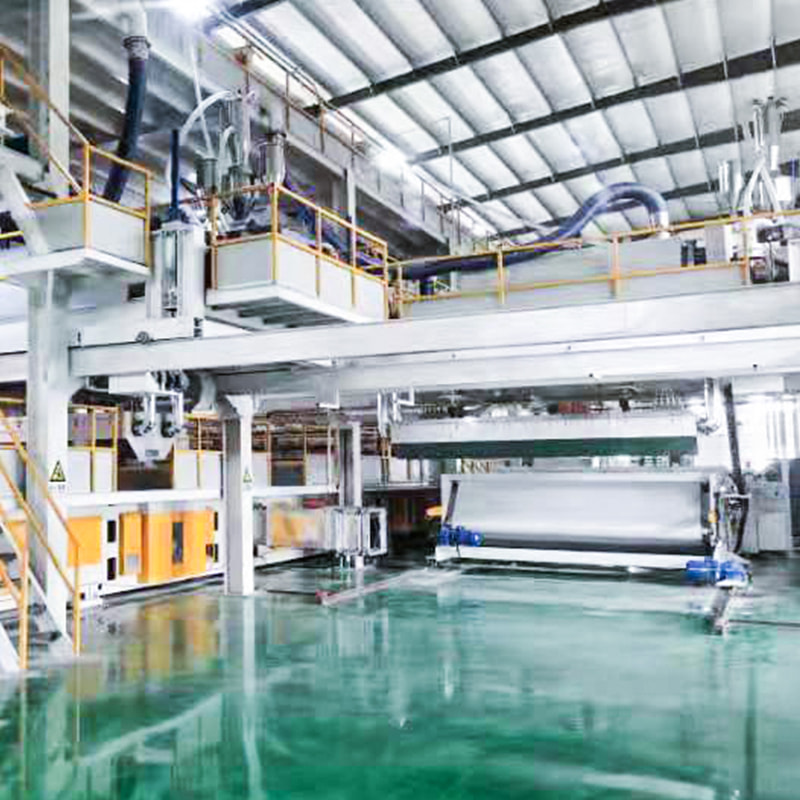
The production of melt blown nonwoven fabric involves extruding molten polymer through fine nozzles, followed by high-velocity hot air stretching to form microfibers. These fibers are collected on a conveyor belt, forming a nonwoven mat.
Key Steps in Production
- Polymer extrusion: Thermoplastic pellets are melted and extruded.
- Fiber formation: High-speed hot air stretches the molten polymer into fine fibers.
- Web collection: Fibers are randomly deposited on a moving conveyor to form a nonwoven web.
- Bonding: Fibers are bonded via thermal, mechanical, or chemical methods to enhance strength.
Properties of Melt Blown Nonwoven Fabric
Melt blown fabrics are known for their unique physical and chemical properties, which make them suitable for critical applications.
Physical Properties
- Ultra-fine fibers with diameters typically between 1-5 microns.
- High porosity with low basis weight.
- Soft and flexible texture.
Functional Properties
- Excellent filtration efficiency for particles and bacteria.
- Hydrophobic or hydrophilic variations depending on polymer type.
- Chemical resistance suitable for industrial applications.
Applications
The unique structure and functionality of melt blown nonwoven fabric enable diverse applications across multiple industries.
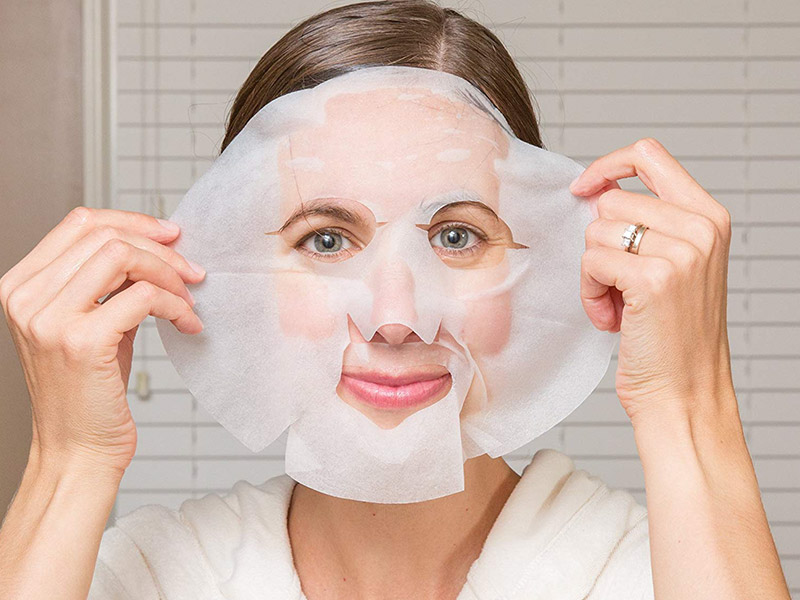
Medical and Healthcare
- Face masks and respirators with high bacterial filtration efficiency.
- Surgical gowns and disposable medical garments.
- Wound dressings and sanitary products.
Industrial Applications
- Air and liquid filtration in HVAC and automotive industries.
- Oil absorbent materials for environmental protection.
- Insulation and reinforcement layers in composite materials.
Comparison with Other Nonwoven Fabrics
Melt blown nonwoven fabrics differ from spunbond and carded nonwovens in fiber diameter, filtration efficiency, and strength.
| Property | Melt Blown | Spunbond | Carded |
| Fiber Diameter | 1-5 μm | 15-35 μm | 20-50 μm |
| Filtration Efficiency | High | Moderate | Low |
| Strength | Moderate | High | Low |
Future Trends
Advancements in polymer technology and electrostatic treatment are enhancing the efficiency of melt blown nonwoven fabrics. The development of biodegradable and reusable versions is expected to expand their environmental applications.






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





