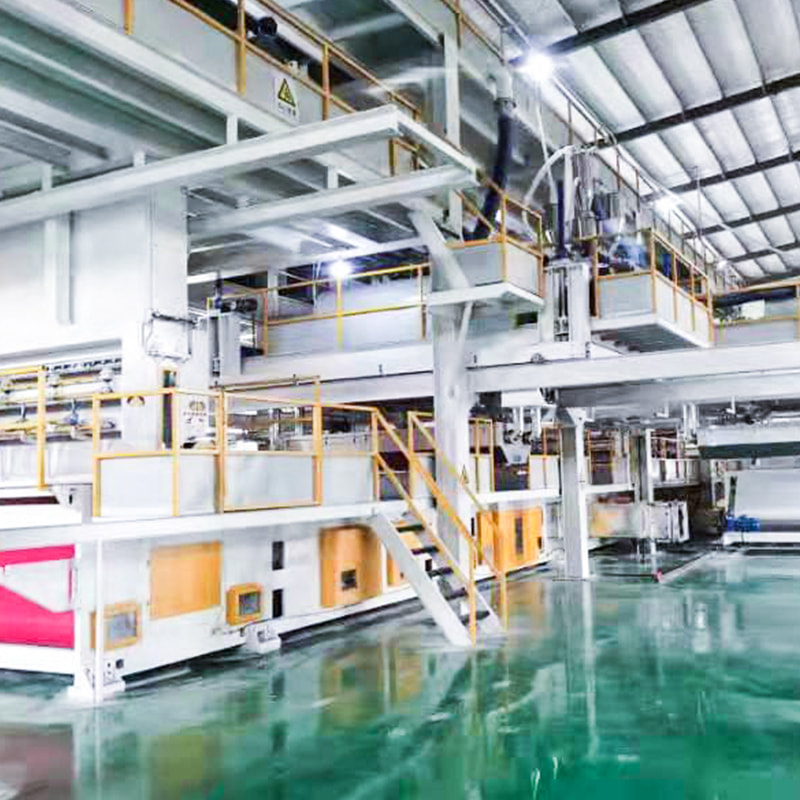
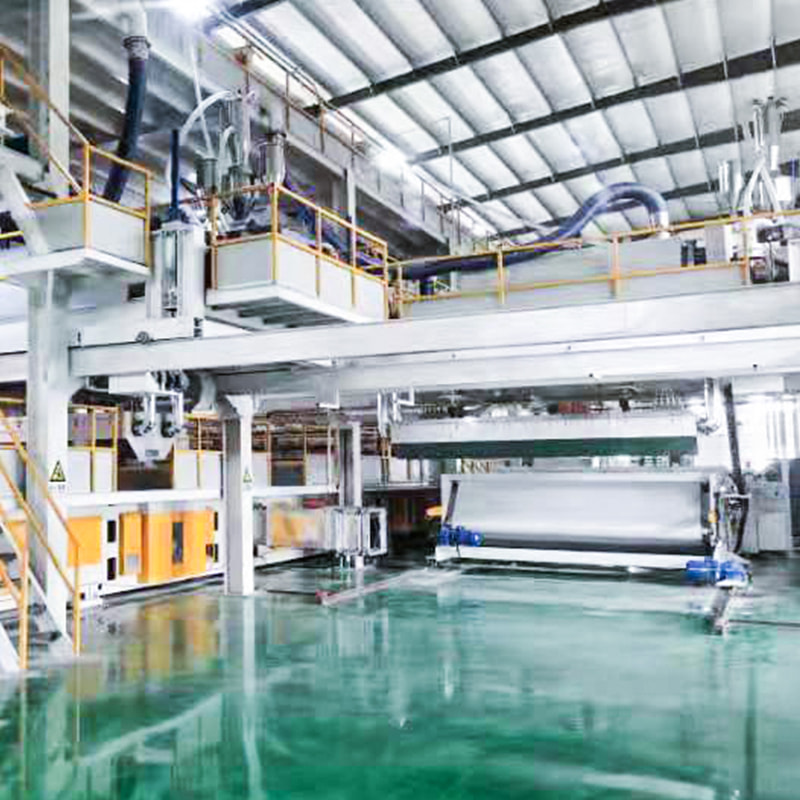
Introduction to Melt Blown Nonwoven Technology
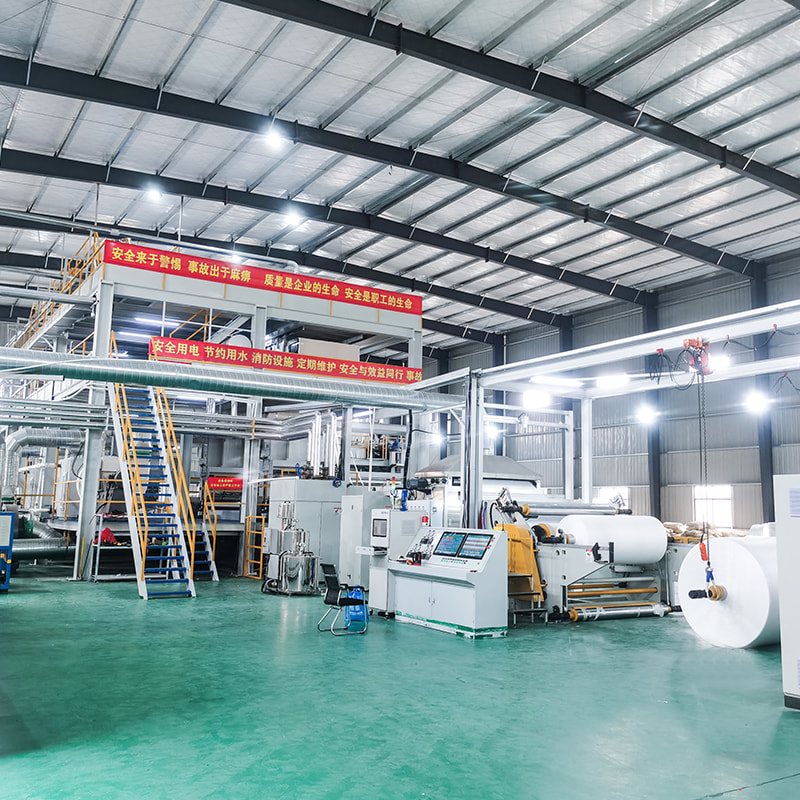
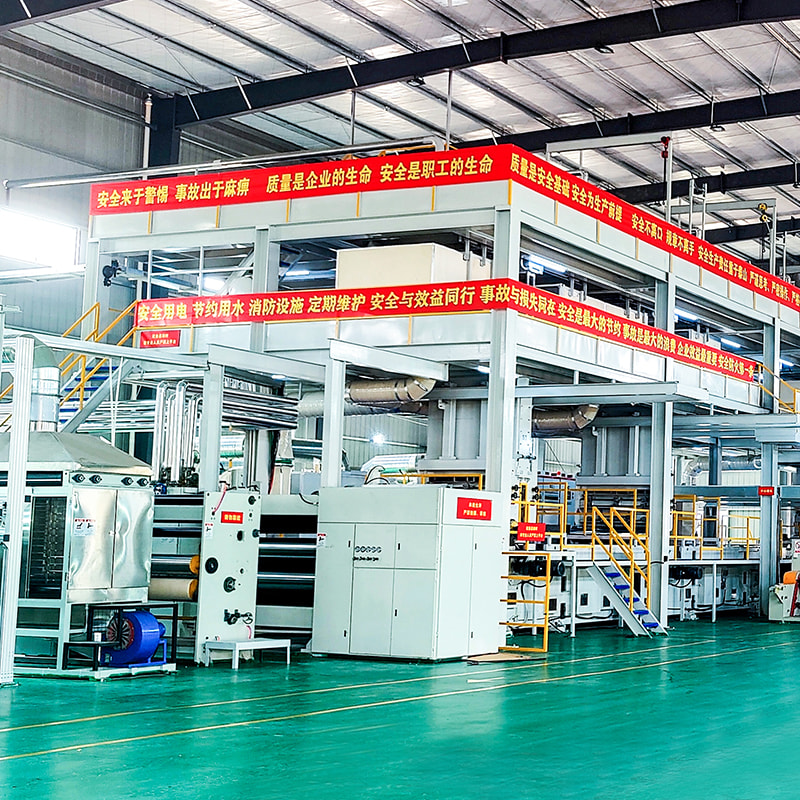
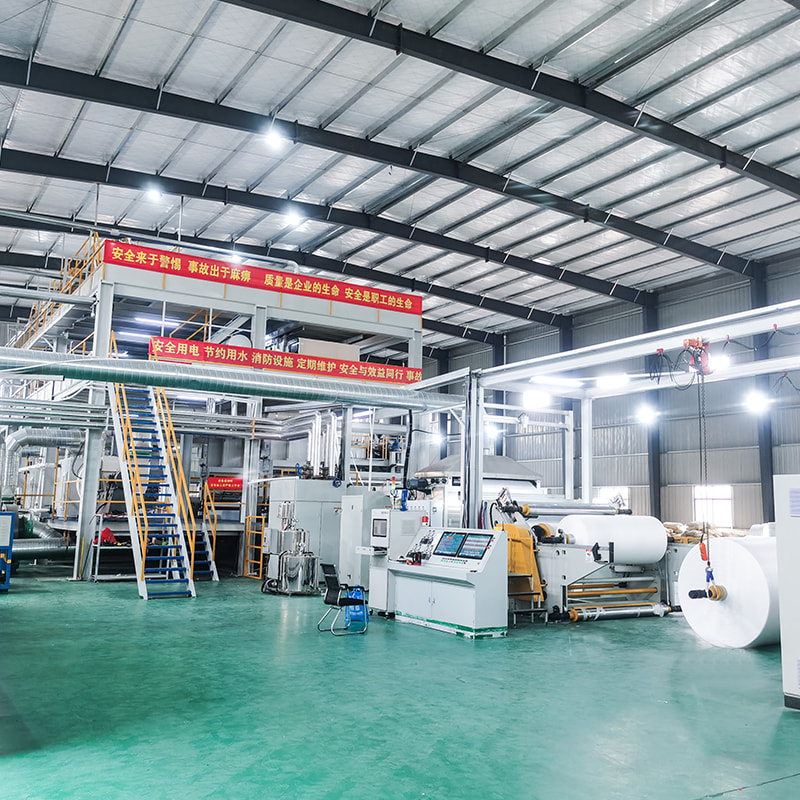
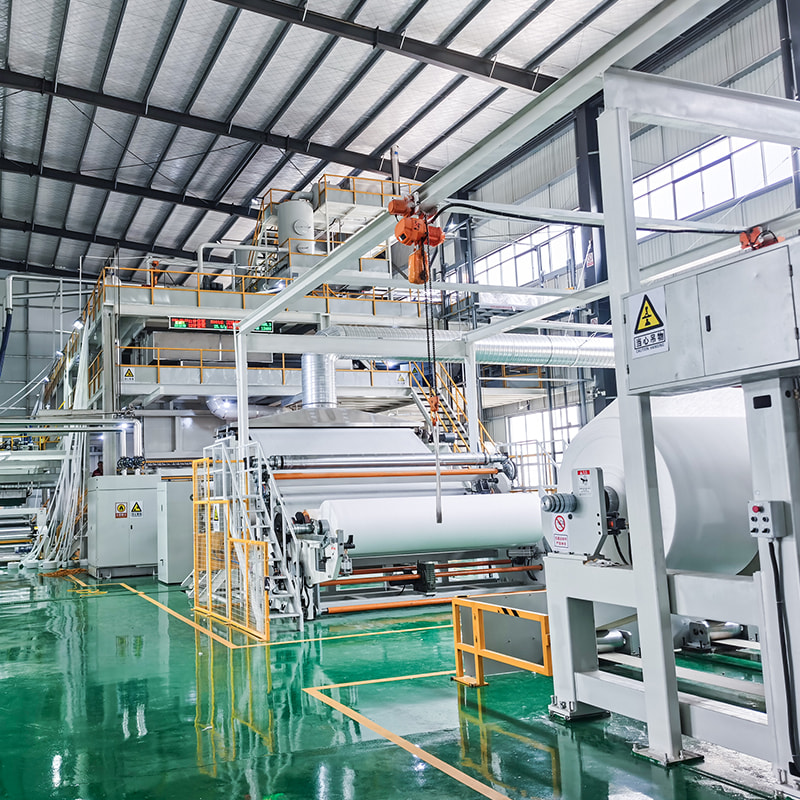
Melt blown nonwoven fabric is a specialized material known for its fine fibers, soft texture, and excellent filtration properties. The production of this fabric relies on advanced machinery called the melt blown nonwoven machine, which processes polymer materials into ultra-fine fibers through a high-speed, controlled extrusion process.
This technology is widely used in industries requiring high-performance filtration, such as medical masks, air filters, oil absorbents, and hygiene products. The unique structure of melt blown fabric—composed of randomly arranged microfibers—provides exceptional barrier properties while maintaining breathability.
Key Specifications of a Melt Blown Nonwoven Machine
A standard melt blown machine operates under precise parameters to ensure consistent fiber quality and fabric performance. Some of the critical specifications include:
Machine Speed: Typically ranges between 10 to 70 meters per minute (M/MIN), depending on the desired fabric weight and fiber fineness.
Filament Denier: Produces extremely fine fibers with diameters ranging from 1.6 to 4 micrometers (μm), much thinner than a human hair.
Fabric Weight: Adjustable between 18 to 300 grams per square meter (GSM), allowing customization for different applications.
Raw Material: Uses polypropylene with a high melt flow index (MFI 800–1600) to ensure smooth extrusion and fine fiber formation.
Delivery Time: Manufacturing and installation typically take 3 to 6 months, depending on machine complexity and customization.
These parameters ensure that the melt blown fabric meets industry standards for filtration efficiency, durability, and softness.
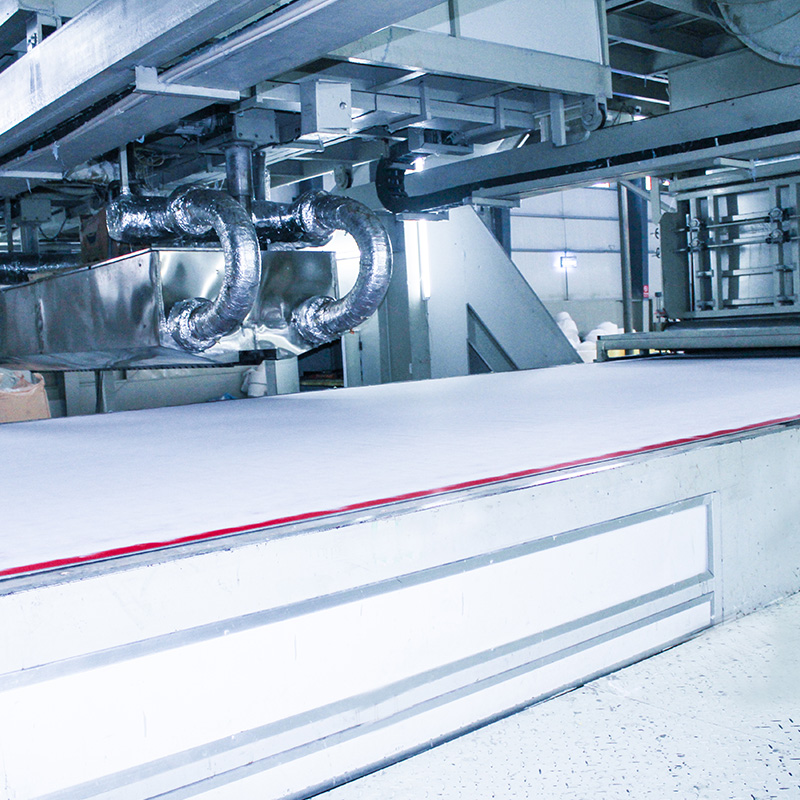

How Melt Blown Nonwoven Fabric is Made
The production of melt blown fabric involves a multi-step process:
Polymer Feeding – Polypropylene pellets with a high melt flow index are fed into the extruder.
Melt Extrusion – The polymer is heated and melted, then forced through a spinneret to form thin strands.
Fiber Formation – High-velocity hot air stretches the molten polymer into ultra-fine fibers.
Fiber Cooling – The fibers cool rapidly as they are blown onto a conveyor belt.
Netting – The fibers randomly accumulate to form a web-like structure.
Reinforcement into Cloth – The web is bonded (either thermally or mechanically) to create a strong, cohesive nonwoven fabric.
The result is a lightweight yet dense material with excellent filtration capabilities due to its fine fiber network.
Applications of Melt Blown Nonwoven Fabric
Thanks to its unique structure, melt blown fabric is used in various high-demand industries:
1. Medical and Hygiene Products
Face masks (especially surgical and N95 respirators) – The fabric’s fine fibers trap microscopic particles, including bacteria and viruses.
Medical gowns and drapes – Provides a protective barrier against fluids and contaminants.
Surgical wraps and sterilization pouches – Ensures sterility in medical equipment packaging.
2. Air and Liquid Filtration
HEPA filters – Used in air purifiers, HVAC systems, and cleanrooms to capture fine dust and pollutants.
Oil-water separation filters – Effective in industrial wastewater treatment due to its hydrophobic properties.
3. Industrial and Consumer Goods
Oil absorbents – Used for spill cleanup in automotive and marine industries.
Insulation materials – Provides thermal and acoustic insulation in construction and appliances.
Wipes and cleaning cloths – Offers high absorbency and durability.
Why Melt Blown Fabric Stands Out
Compared to other nonwoven materials, melt blown fabric has distinct advantages:
Ultra-Fine Fibers – The microfibers create a dense network that enhances filtration efficiency.
High Surface Area – The random fiber arrangement increases particle capture capacity.
Soft and Elastic – Comfortable for medical and hygiene applications.
Customizable Weight and Thickness – Can be engineered for specific performance needs.






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





