Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabric: Applications and Insights
Nonwoven fabrics have grown in significance over the years, owing to their versatile and innovative applications in various industries. Among the numerous methods for manufacturing nonwoven fabrics, spunmelt technology stands out due to its efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and range of applications. In this article, we'll explore the key features of spunmelt nonwoven fabrics, the technology behind them, and their applications across different industries.
What is Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabric?
Spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are created through a unique process that combines the principles of both spunbond and meltblown technologies. These fabrics are produced without the need for weaving or knitting, making them a highly efficient and cost-effective solution for a variety of uses.
Spunbond Process: In this method, thermoplastic polymers are extruded into continuous filaments that are then laid out in a random pattern and bonded together using heat or pressure.
Meltblown Process: This process involves extruding polymer through fine nozzles at high pressure, resulting in extremely fine fibers. These fibers are then bonded together through their own heat or pressure to form the fabric.
The spunmelt process combines the spunbond and meltblown methods, creating a fabric that incorporates the characteristics of both. Spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are highly durable, breathable, and versatile.
Key Properties of Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabrics
Lightweight and Flexible: Spunmelt fabrics are lightweight and easy to handle, making them suitable for a variety of applications, especially in the medical and hygiene sectors.
High Tensile Strength: The fabric's structure, composed of continuous fibers, provides high strength and resistance to tearing, making it suitable for applications where durability is essential.
Breathability and Softness: Thanks to the fine fibers produced during the meltblown process, spunmelt nonwoven fabrics exhibit superior breathability, comfort, and softness, which is especially important in personal care products.
Water Resistance and Absorbency: Depending on the specific polymer used, spunmelt fabrics can be engineered to have excellent water resistance or enhanced absorbency, crucial for applications in hygiene and medical products.
Customization: The spunmelt process allows for a wide range of fabric weights, thicknesses, and surface finishes, offering flexibility in tailoring materials for specific uses.
Applications of Spunmelt Nonwoven Fabrics
The versatility of spunmelt nonwoven fabrics enables their use across a variety of industries, each with specific needs for performance, safety, and reliability. Below, we’ll explore some of the key applications:
1. Medical and Healthcare Industry
Spunmelt fabrics are widely used in medical and healthcare applications due to their hygiene, barrier properties, and soft texture.
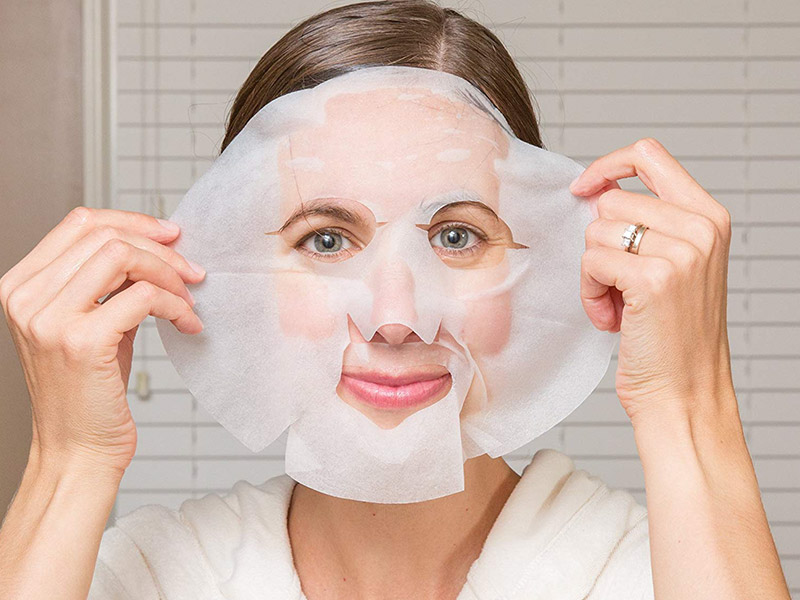
Face Masks and Respirators: Spunmelt fabrics are commonly used in the production of face masks and respirators due to their excellent filtration properties. The fine fibers created during the meltblown process are effective at trapping microscopic particles, making these fabrics ideal for high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters.
Surgical Gowns and Drapes: These fabrics are also used in disposable surgical gowns, drapes, and sterile medical covers, providing a barrier against bacteria and viruses while maintaining comfort and breathability for the wearer.
Wound Dressings: The absorbent nature of spunmelt fabrics, especially when engineered to be highly porous, makes them ideal for use in wound care products, where moisture management is essential for healing.
2. Hygiene Products
The hygiene sector is one of the largest consumers of spunmelt nonwoven fabrics, particularly in disposable personal care products.
Diapers and Adult Incontinence Products: Spunmelt fabrics are a key component in the construction of diapers, adult incontinence pads, and feminine hygiene products. The fabric provides softness, comfort, and moisture management, which is critical for skin protection and hygiene.
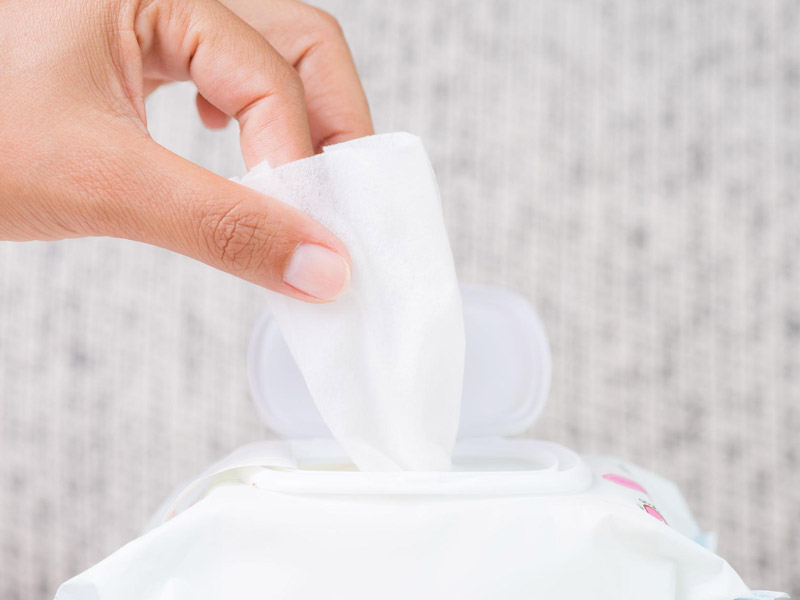
Wet Wipes: The absorbent and soft nature of spunmelt fabrics makes them perfect for wet wipes, which are used for a wide range of applications, from baby care to personal hygiene and cleaning.
3. Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are used for various interior components, providing benefits like lightweight construction and noise reduction.
Sound Insulation and Acoustic Fabrics: Due to their ability to absorb sound, spunmelt fabrics are often used as soundproofing or insulation materials in vehicles.
Interior Upholstery: The softness and durability of spunmelt fabrics make them ideal for use in automotive seats, headliners, and trim fabrics, improving both comfort and aesthetic appeal.
Filtration Systems: Spunmelt materials are also used in air filters, oil filters, and cabin filters, where their ability to capture fine particles is crucial.
4. Building and Construction
In construction, spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are used for a range of applications, contributing to improved durability and performance in various building materials.
Roofing and Geotextiles: Spunmelt fabrics are often used as a layer in roofing systems and as geotextiles to prevent soil erosion. Their strength and resistance to environmental factors make them ideal for outdoor applications.
Insulation Materials: Due to their excellent thermal properties, spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are employed in insulation products, where they help regulate temperature and energy efficiency.
5. Packaging Industry
Spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are increasingly used in the packaging industry, particularly in applications requiring breathable and protective materials.
Protective Packaging: The flexibility, durability, and moisture-resistant properties of spunmelt fabrics make them perfect for protective packaging, especially for sensitive or fragile goods that require moisture and dust protection.
Agricultural Packaging: Nonwoven fabrics are used for agricultural purposes, such as protective covers for plants or as part of soil improvement products.
6. Filter Media
In industrial and environmental applications, spunmelt nonwoven fabrics are used as filter media, thanks to their excellent filtration properties.
Air and Liquid Filtration: The fine fibers produced in the meltblown process are capable of filtering out tiny particles, making these fabrics ideal for air filtration systems, such as in HVAC systems or industrial air purifiers.
Water Filtration: Spunmelt fabrics are also used in water filtration systems, where their ability to trap contaminants is crucial for producing clean and safe drinking water.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of spunmelt nonwoven fabrics is promising, with ongoing innovations and advancements in technology driving further expansion of their applications.
Biodegradable Materials: As sustainability becomes a greater concern, there is increasing demand for spunmelt fabrics made from biodegradable polymers. This trend is particularly significant in the hygiene and packaging industries, where environmental impact is a growing consideration.
Smart Textiles: With the rise of wearable technology, there is an interest in integrating sensors, conductive materials, or other smart elements into spunmelt fabrics, opening new possibilities for medical, sports, and military applications.
High-Performance Filtration: With growing concerns around air quality, particularly in urban environments, the demand for high-efficiency filters will drive further innovations in spunmelt materials, leading to enhanced filtration capabilities.
Sustainability in Production: The shift toward greener manufacturing processes, including reduced energy consumption and the use of recycled raw materials, will be crucial as industries continue to prioritize sustainability.






 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский عربى
عربى





